Search results
Author(s):
Robert-Jan van Geuns
Added:
6 years ago
Robert-Jan van Geuns from Erasmus Medical Centre, Rotterdam, The Netherlands disusses BIVAL: Bivalirudin infusion for ventricular infarction limitation: the BIVAL study.
Filmed by Radcliffe Cardiology on-site at EuroPCR 2017.
View more
Management of Haemostasis with Combined Use of Vascular Closure Devices and Bivalirudin - A Review
Author(s):
Emanuela de Cillis
,
Giuseppe Sangiorgi
,
Alessandro Santo Bortone
Added:
3 years ago
Article
Author(s):
Eunice NC Onwordi
,
Amr Gamal
,
Azfar Zaman
Added:
3 years ago
Acute coronary syndromes (ACS) are a major cause of morbidity and mortality. Despite the use of optimal medical therapy and revascularisation there remains a significant risk of vascular events. Registry data indicates a persistent risk even in patients who are event free in the first year following ACS, with as many as 1 in 5 patients suffering a vascular event in the subsequent 3 years.1
The…
View more
Author(s):
Benjamin Galper
,
Roxana Mehran
Added:
3 years ago
Acute coronary syndromes (ACS) result from unstable coronary artery plaques that rupture and can lead to coronary ischaemia, unstable angina and myocardial infarction. The treatment goals in ACS focus on reducing ischaemia, preventing further progression of thrombotic plaque by disturbing the milieu of thrombosis and platelet aggregation taking place within the coronary artery and, in the case of…
View more
Author(s):
Sri Raveen Kandan
,
Thomas W Johnson
Added:
3 years ago
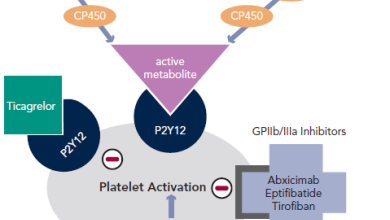
Antiplatelet Therapy
Current guidelines support the early administration of oral antiplatelet agents upstream of angiographic assessment and intervention.1 Aspirin is commonly given by the first medical contact and additional oral antiplatelet drugs are administered on arrival in hospital (see Figure 1).
Aspirin
The efficacy of aspirin in acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)…
View more
Author(s):
Steven V Manoukian
,
Michele D Voeltz
,
Frederick Feit
Added:
3 years ago
Non-ST-segment elevation (NSTE) acute coronary syndromes (ACS) include unstable angina (UA) and NSTE myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), and account for one and a half million hospitalisations in the US annually. Patients with ACS are typically managed by initial medical stabilisation followed by an early invasive approach, whereby cardiac catheterisation is performed, usually within 24 hours of…
View more
Optimum Therapies for ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Managed with Primary Percutaneous Coronary…
Author(s):
Bruce R Brodie
Added:
3 years ago
Article
Early Stent Thrombosis after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention for Acute Myocardial Infarction
Author(s):
Georgios J Vlachojannis
,
Bimmer E Claessen
,
George D Dangas
Added:
3 years ago
Article
Author(s):
Fizzah A Choudry
,
Roshan P Weerackody
,
Daniel A Jones
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
Over the last few decades, primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) has revolutionised the treatment of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) with rapid recanalisation of the infarct-related epicardial vessel, resulting in smaller infarct size and a substantial reduction in adverse clinical endpoints.1,2 However, suboptimal myocardial reperfusion is documented to occur in a…
View more
Stefan James
Job title: Professor of Cardiology
Author